In this scenario we want to know the computer go through Network device as Switch/Router to access Internet.
Based on Cisco device, write down the relation learning information for the reference.
 Setting an IP on the WAN/LAN interface
Step 1.
Setting an IP on the WAN/LAN interface
Step 1. Define Fast Ethernet 0/0 with an IP address as 192.168.10.171 by using the following command.

So does that the configuration will be changed as follows:
AS-IS

TO-BE
 Step 2.
Step 2. Define Ethernet 2/0 with an IP address as 10.10.101.253 by using the following command.
 Setting Static default Route
Step 3.
Setting Static default Route
Step 3. Due to assign the IP address manually, we have to define a default route by using the
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.254 command
 Defining NAT inside and outside interfaces
Step 4.
Defining NAT inside and outside interfaces
Step 4. Define Fast Ethernet 0/0 as a NAT outside interface by using the following command.
 Step 5.
Step 5. Define Ethernet 2/0 as a NAT inside interface by using the following command.
 Define Inside global IP Address Range
Define Inside global IP Address Range (
with no-overload or overload)
Step 6. Define a NAT pool named as no-overload with a range of addresses 192.168.10.200 ~ 192.168.10.240 by using the
ip nat pool <pool name> <strart ip> <end ip> prefix <prefix length> command
 Define Inside local IP Address Range
Step 7.
Define Inside local IP Address Range
Step 7. Define Access List 6 that it permit packets with source addresses ranging from 10.10.103.0 to 10.10.103.255
 Define the relationship of between Inside local and Inside global
Step 8.
Define the relationship of between Inside local and Inside global
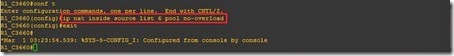
Step 8. Define “Access list 6” address can NAT to a pool “no-overload” by using the
ip nat inside source list <access list number> pool <pool name> command
To verify the NAT translations in the router by using the
show ip nat translations command

To clear dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) translations from the translation table by using the
clear ip nat translations * command
 Reference
Reference
(# 1) The keyword
overload used in the
ip nat inside source list 103 pool ovrld overload command allows NAT to translate multiple inside devices to the single address in the pool.
(# 2) Protocols with Access Lists Specified by Numbers
| Protocol | Range |
| IP | 1 to 99 |
| Extended IP | 100 to 199 |
| Ethernet type code | 200 to 299 |
| Ethernet address | 700 to 799 |
| Transparent bridging (protocol type) | 200 to 299 |
| Transparent bridging (vendor code) | 700 to 799 |
| Extended transparent bridging | 1100 to 1199 |
| DECnet and extended DECnet | 300 to 399 |
| XNS | 400 to 499 |
| Extended XNS | 500 to 599 |
| AppleTalk | 600 to 699 |
| Source-route bridging (protocol type) | 200 to 299 |
| Source-route bridging (vendor code) | 700 to 799 |
| IPX | 800 to 899 |
| Extended IPX | 900 to 999 |
| IPX SAP | 1000 to 1099 |
| Standard VINES | 1 to 100 |
| Extended VINES | 101 to 200 |
| Simple VINES | 201 to 300 |















































