The time correction is very important on any systems as tracking log between servers, business data flow, Kerberos authentication and so on. For this reason, I will build a internal time server as bridgehead to synchronize the time between servers and clients.
Which one is chosen about Time Server? The NTPD(Network Time Protocol Daemon) will be best choice on Linux platform.
How to do it? The general process is that first install & configure ntpd, then correct the current time/zone on this server, adjust the firewall rule, configure ntpd on server boot, and verify whether the function is normal.
Install NTP via tarball
Prerequisite
To create a new ntp group with a specific groupid by using the
groupadd –g 38 ntp command

To create a new ntp user with specific userid by using the
useradd –d /etc/ntp –u 38 –g ntp –s /sbin/nologin ntp command

To install the Development tools for compiling any application by using the
yum groupinstall “Development tools” command
 Compile & Install
Compile & Install
To download a recent NTP tarfile from NTP home page
http://www.ntp.org/ and extract this compressed package in the
/tmp directory by using the
tar –zxvf ntp-4.2.6p5.tar.gz command

So does that the ntp source tree will be created. To switch to the distribution base directory for making this software.

To configure sources for performing an automatic configuration procedure that inspect the hardware & software environment and configure the build process by using
./configure - -prefix=/usr - -sysconfdir=/etc - -with-binsubdir=sbin - -with-lineeditlibs=readline - - enable-clockctl command (# 1)


To compile and link the distribution sources by using
make command


To install ntp by using
make install command so that the executable file by default is in the
/usr/local/bin directory

 Set Permission and Parameter
Set Permission and Parameter
To create a
/var/lib/ntp directory next to set the directory permission to 755 by
using the chmod 755 /var/lib/ntp command and change the UIG:GID for
/var/lib/ntp to
ntp:ntp by using the
chown –v ntp:ntp /var/lib/ntp command

To change the
/var/run/ntpd.pid UIG:GID to ntp:ntp by using the
chown ntp:ntp /var/run/ntpd.pid command
To create a
/etc/sysconfig/ntpd directory and add some parameters for passing argument to the
ntpd daemon at boot time.

To create a
/etc/ntp/crypto directory, the
/etc/ntp/crypto/pw &
/etc/ntp/keys file and change the owner & permission to this directory
Install NTP via yum
To install ntpd by using the
yum install ntp command


Configure NTP via tarball or yum
After finish the above one installation, we have to modify or add the
/etc/ntp.conf file based on our environment by using
vi /etc/ntp.conf command. (# 2)
The following expression is different result before- and after- modify the
ntp.conf file.
AS-IS

TO-BE
 Adjust iptables for NTP
Adjust iptables for NTP
To add a firewall rule by using the iptables command that will open the UDP port 123 for allowing this NTP server communicate with the internal client and external time server.


Due to the above command just temporarily store in memory, we have to execute the
service iptables save command that avoid the new rule miss after the system reboot. For applying the new rule, we will restart iptables daemon by using the
service iptables restart command.

The following expression is different result before- and after- do the iptables command.
AS-IS

TO-BE

Start NTP automatically
If the ntp is installed via tarball, we need to create a
/etc/init.d/ntpd file and add some content as follows next to set this file permission to 755
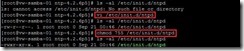
/etc/init.d/ntpd


To set ntp daemon to auto start on boot by using the
chkconfig ntpd on command

If the ntp is installed via yum,we can update chkconfig by executing the
chkconfig - - level 235 on command so that the ntp will start automatically on the system startup.
 Start NTP manually
Start NTP manually
If the ntp is installed via tarball, we can start this daemon by using the
/etc/init.d/ntpd start command

If the ntp is installed via yum,we can start it by using the
/etc/init.d/ntpd start or
service ntpd start command

Verify NTP mechanism
To realize whether the ntp daemon is running now by using the
service ntpd status command.

To confirm whether the system clock can synchronize the outside time server by using the
ntpstat command.

To realize the relationship between the ntp and up time server by using the
ntpd –p command. (# 3)

To realize whether the UDP port 123 is listening now by using the
netstat –unlnp | grep 123 command

Until now, we have already finish NTP daemon setup and installation.
Reference :
(# 1) If execute configure command without the - - enable-clockctl parameter, we will get the error when start ntpd daemon.

(# 2) If we want to configure NTP time server in
/etc/ntp.conf, maybe we can refer to the
NTP Pool Project Web Site and choose the neighboring time server as Asia for us.

To choose the neighbor zone as Taiwan

So does that we can add the pool zone to the
/etc/ntp.conf file

(# 3) If it have no a NTP drift file after time correction, we have to create a drift file manually by using the
echo 0 > /var/lib/ntp/drift command

and change the UIG:GID to
ntp:ntp by using the
chown ntp:ntp /var/lib/ntp/drift command

 To reload the clock right now by using the source /etc/sysconfig/clock command and copy the right timezone file as Asia/Taipei under the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory to the /etc directory by using the cp –p /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia /etc/localtime command.
To reload the clock right now by using the source /etc/sysconfig/clock command and copy the right timezone file as Asia/Taipei under the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory to the /etc directory by using the cp –p /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia /etc/localtime command.
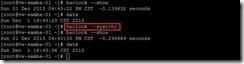 So does that the accurate time will be kept after reboot.
So does that the accurate time will be kept after reboot.

































