Prerequisite
To login the system by root account and update the yum repositories and packages by using the yum update command.
 If the process complete, please reboot for applying the update.
If the process complete, please reboot for applying the update.To disable SELinux for reducing complications issue
 To change FQDN name in the /etc/sysconfig/network file that depend on our requirement
To change FQDN name in the /etc/sysconfig/network file that depend on our requirement To install the related packages with dependencies for installing and building Samba 4 tarball by using the
To install the related packages with dependencies for installing and building Samba 4 tarball by using the yum -y install gcc make wget python-devel gnutls-devel openssl-devel libacl-devel krb5-server krb5-libs krb5-workstation bind bind-libs bind-utils command (# 2)
To query the rpm database to find any older samba package by using the rpm –qa | grep samba or yum list installed | grep samba commandDownload, compile & install Samba 4
Option (1):To download manually the latest Samba tarball from the Samba Website
 To unpack and decompress this download tarball by using the command tar –zxvf smaba-x.x.x.tar.gz
To unpack and decompress this download tarball by using the command tar –zxvf smaba-x.x.x.tar.gz or the git clone http://gitweb.samba.org/samba.git samba-master command (# 4)
or the git clone http://gitweb.samba.org/samba.git samba-master command (# 4)After finish any option, we have to switch to the extracted directory next to configure it by executing the command ./configure - -enable-selftest
 To build Samba by using the command make
To build Samba by using the command make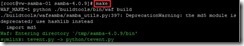
 To install Samba by using the command make install
To install Samba by using the command make install
 So does that the Samba will be installed to the /usr/local/samba directory (# 5)
So does that the Samba will be installed to the /usr/local/samba directory (# 5)Provision Samba 4.0.x
To provision a new domain by executing the command /usr/local/samba/bin/samba-tool domain provision and change the default setting if necessary (# 6)

Configure Samba 4 with Bind as DNS backend
To setup Bind 9 folder permission as follows:
 Edit Bind9 configuration
Edit Bind9 configurationTo append
include "/usr/local/samba/private/named.conf"; at the end of the file and add tkey-gssapi-keytab "/usr/local/samba/private/dns.keytab"; to the options by editing /etc/named.conf Configure rndc
Configure rndcTo generate rndc.key in the /etc directory by executing the rndc-confgen –a –r /dev/urandom command it this key never appear.
To generate rndc.conf in the /etc directory by running the rndc-confgen > /etc/rndc.conf command
 To correct rndc.key secret value is the same as one in the /etc/rndc.conf file
To correct rndc.key secret value is the same as one in the /etc/rndc.conf file And by editing the /etc/named.conf file, we need to add some value that the content is the same as one in the /etc/rndc.conf file (# 7)
And by editing the /etc/named.conf file, we need to add some value that the content is the same as one in the /etc/rndc.conf file (# 7) If the above process finish, we will rename or delete rndc.conf file to avoid the confusion.
If the above process finish, we will rename or delete rndc.conf file to avoid the confusion.Add Reverse Zone Record
Due to this is the fist DNS Server that is built with Samba Server, we have to add some record as Reverse Zone for configuring Primary(Master) Name Server by editing /etc/named.conf file
 Create Zone file
Create Zone fileBased on our mention in the additional record of the /etc/named.conf file, we will create rev.dwlab.mooo.com file in the /var/named directory and add the entries for reverse zone.
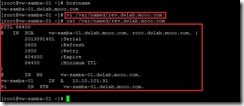 Also create rev.localhost file in the /var/named directory and add the entries for reverse zone.
Also create rev.localhost file in the /var/named directory and add the entries for reverse zone.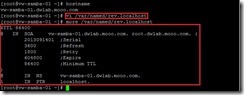
Start Bind Service
To start named service by executing the service named start or /etc/init.d/named start command manually

Verify DNS function
To set the samba will use the own internal DNS firstly by editing the /etc/sysconfig/network-script/ifcfg-eth0 file
 To confirm whether named daemon is started by using the service named status command
To confirm whether named daemon is started by using the service named status command To verify whether the forward and reverse lookup is right by executing nslookup command
To verify whether the forward and reverse lookup is right by executing nslookup command
Install and Configure NTP
Due to the time synchronization between DC and Client is very important, we need to enable NTP daemon in each Samba 4 as AD role.
How to do it? please refer to this article NTP --- Install & Configure NTP daemon on Minimal CentOS 6.x to realize it in detail
Configure Kerberos
Due to the kerberos in CentOS 6.3 or later is handled by the /etc/krb5.conf file,we will backup this original file and replace it with the /usr/local/samba/setup/krb5.conf file
 To edit the /etc/krb5.conf file and replace ${REALM} with the value you chose for the '--realm' parameter of the provision command earlier
To edit the /etc/krb5.conf file and replace ${REALM} with the value you chose for the '--realm' parameter of the provision command earlier
Configure & Start Samba 4
Start Samba 4 manually
To start manually the samba daemon by using the /usr/local/samba/sbin/samba command


 To set this init script permission to 755 by using the chmod 755 /etc/init.d/samba4 command
To set this init script permission to 755 by using the chmod 755 /etc/init.d/samba4 command To start manually the samba daemon by using the /etc/init.d/samba4 start command
To start manually the samba daemon by using the /etc/init.d/samba4 start commandStart Samba 4 automatically
To start it at boot by appending the /usr/local/samba/sbin/samba command to the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file
To initialize samba daemon start at boot by using the chkconfig - - levels 235 samba4 on command if we ever create a samba init script.
Configure iptables rule
To realize which listening port require for AD/Samba4 by using the netstat –lntup | grep –e samba –e smbd command
 or for DNS by using the netstat –lntup | grep –e named command
or for DNS by using the netstat –lntup | grep –e named command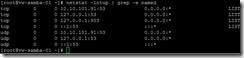 or for NTP by using the netstat –lntup | grep –e ntpd command
or for NTP by using the netstat –lntup | grep –e ntpd command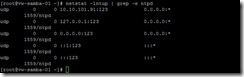 So do we can summarize what port number needs as follows:
So do we can summarize what port number needs as follows:53, TCP & UDP (DNS)
88, TCP & UDP (Kerberos authentication)
123, TCP & UDP (NTP)
135, TCP (MS RPC)
137, UDP (NetBIOS name service)
138, UDP (NetBIOS datagram service)
139, TCP (NetBIOS session service)
389, TCP & UDP (LDAP)
445, TCP (MS-DS AD/SMB CIFS)
464, TCP & UDP (Kerberos change/set password)
636, TCP (LDAP SSL)
3268, TCP (LDAP Global Catalog)
3269, TCP (LDAP Global Catalog SSL)
To add the above port number to the iptables rule by executing the following command
 or directly add iptables rules to the /etc/sysconfig/iptables file
or directly add iptables rules to the /etc/sysconfig/iptables fileDon’t forget to execute the service iptables save and service iptables restart command for applying the new rule right now. (# 8)
Verify Samba 4 AD DC
Test Samba
To confirm the samba version by using the /usr/local/samba/sbin/samba –V command

Test DNS
To confirm the DNS record for ldap, kerberos and samba by using the following command.

Test Kerberos
To confirm whether kerberos authentication is working by using the kinit administrator@DWLAB.MOOO.COM command (# 9)

Until now, we have already finished building the Samba 4 AD DC!
Reference :
(# 1) If we has interesting to realize what the new changes in Samba 4, please refer to this Samba WiKi
(# 2) Which the development library and program need to be installed? Maybe we can refer to this web site Samba 4/OS Requirements to find the solution.
(# 3) If the samba ever is installed by yum, we will see what packages have already been existed now by using the rpm –qa | grep samba or yum list installed | grep samba command
 (# 4) In general, the git protocol is the preferred choice because the download data is compressed.
(# 4) In general, the git protocol is the preferred choice because the download data is compressed.(# 5) When we need to install the necessary missing packages for fix error that run configure, make, make install command,please remember to do make clean command before running make again
(# 6) If we need to re-run the provision command, we have to remove the /usr/local/samba/etc/smb.conf file ,and Samba database by using the command rm –rf /usr/local/samba/private/*
(# 7) If no add these values, maybe we will get the error message as follows when run the service named status command
AS-IS
 TO-BE
TO-BE
 (# 9) please note the domain realm have to be uppercase letters as DWLAB.MOOO.COM. If key in lowercase letters as dwlab.moo.com, we will get the error message as follows:
(# 9) please note the domain realm have to be uppercase letters as DWLAB.MOOO.COM. If key in lowercase letters as dwlab.moo.com, we will get the error message as follows: