In Windows Server 2012, there is one new feature in Hyper-V that is live migration without Shared Storage. It is good news for us to use live migration on Non-Clustered environment so that I will build a lab for this testing.
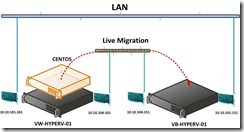
At first, we need to prepare something before begin to do the live migration lab.
Prerequisites:
● Install Windows Server 2012 with Hyper-V role on the source and destination host
● In the source host, at least one virtual machine is alive then.
● The source and destination host join into the same domain, or exist on the different domain that these domains trust each other.
● To manage the Hyper-V task by remote management tools (# 1), we have to configure constrained delegation and select Kerberos as the authentication protocol. so the operator account that want to configure constrained delegation need to be a member of the Domain Administrators group.
● To configure or perform live migration, the operator account must be a member of the local Hyper-V Administrator group or Administrators group on both the source and destination host.
After finish the above prerequisites, we will begin to do the following process based on
[Scenario 1]:To use Kerberos to authenticate live migration traffic
Step 1:Configure constrained delegation
(1). Log on an account that is a member of the Domain Administrator Group and open Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in
(2). In the Computers folder, right-click the computer account of the source server and then click Properties in menu
 (3). In the delegation tab, select Trust this computer for delegation to the specified services only and Use Kerberos only under the above option next to click Add button
(3). In the delegation tab, select Trust this computer for delegation to the specified services only and Use Kerberos only under the above option next to click Add button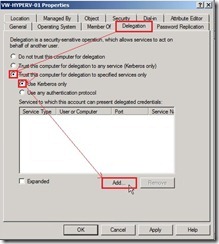 (4). In the Add Service window, click Users or Computers… button
(4). In the Add Service window, click Users or Computers… button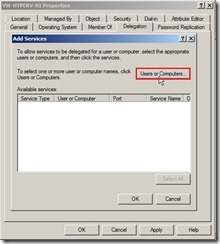 (5). In Select Users or Computers dialog box, type the name of the destination server, then click Check Names to verify the typed name is correct or not next to click OK button
(5). In Select Users or Computers dialog box, type the name of the destination server, then click Check Names to verify the typed name is correct or not next to click OK button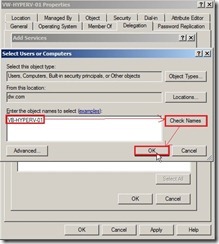 (6). In the list of available services, select cifs next to click OK button if we want to move virtual machine storage along with the virtual machine, or if we want to move only a virtual machine’s storage, or if we use SMB storage for Hyper-V.
(6). In the list of available services, select cifs next to click OK button if we want to move virtual machine storage along with the virtual machine, or if we want to move only a virtual machine’s storage, or if we use SMB storage for Hyper-V.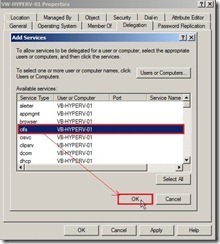 (7). To type the name of the destination server again by click Users or Computers… button, then select Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service in the available services list next to click OK button if we want to move virtual machines.
(7). To type the name of the destination server again by click Users or Computers… button, then select Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service in the available services list next to click OK button if we want to move virtual machines. 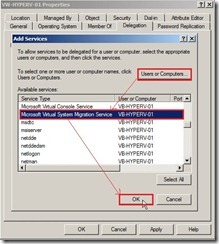 (8). In the Delegation tab of the Source Server, the cifs and Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service in the Destination Server will be listed. Click OK button to completely configure constrained delegation for Source Server.
(8). In the Delegation tab of the Source Server, the cifs and Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service in the Destination Server will be listed. Click OK button to completely configure constrained delegation for Source Server.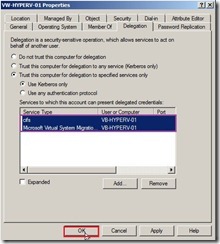 (9). Repeat the above process to add the Destination Server’s cifs and Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service into the Delegation tab of the Source Server.
(9). Repeat the above process to add the Destination Server’s cifs and Microsoft Virtual System Migration Service into the Delegation tab of the Source Server.
Step 2: Configure Live Migration
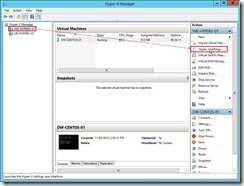
(1). Open Hyper-V Manager, select a Source Server that we want to configure live migration next to click Hyper-V Settings… In the Action pane.
 (2). In Hyper-V Setting dialog box, click Live Migrations next to choose Enable incoming and outgoing live migrations check box, select User Kerberos option if we have configured constrained delegation, keep default value under Simultaneous live migrations, select Use these IP addresses for live migration option and click Add button for using specific network connection to accept live migration traffic.
(2). In Hyper-V Setting dialog box, click Live Migrations next to choose Enable incoming and outgoing live migrations check box, select User Kerberos option if we have configured constrained delegation, keep default value under Simultaneous live migrations, select Use these IP addresses for live migration option and click Add button for using specific network connection to accept live migration traffic.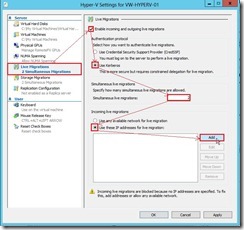 (3). In IP Address dialog box, we will set an IP address as “10.10.104.101” that belongs to the second network card next to click OK button
(3). In IP Address dialog box, we will set an IP address as “10.10.104.101” that belongs to the second network card next to click OK button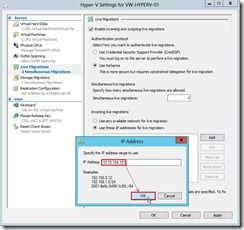 (4). click OK button to complete Live Migrations configuration in the Source Server
(4). click OK button to complete Live Migrations configuration in the Source Server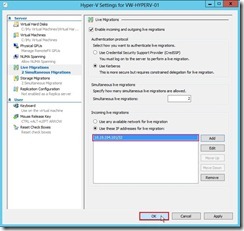 (5). Repeat the above process in Destination Server for configuring live migration.
(5). Repeat the above process in Destination Server for configuring live migration.
Step 3: Configure Inbound Firewall Rule (1). By default, the Hyper-V (MIG-TCP-In) firewall rule will be added automatically in Inbound rule when we configure live migration setting in Hyper-V Manager.
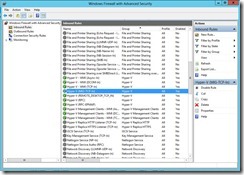 (2). If no exist this rule, we have to right-click Inbound Rules next to click New Rule… by opening Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (# 2).
(2). If no exist this rule, we have to right-click Inbound Rules next to click New Rule… by opening Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (# 2).
Step 4: Move a running virtual machine (# 3) (1). From the Virtual Machines section of Hyper-V Manager, right-click the virtual machine and then click Move
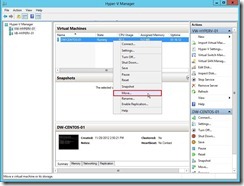 (2). On the Before You Begin page of the Move Wizard, click Next > button
(2). On the Before You Begin page of the Move Wizard, click Next > button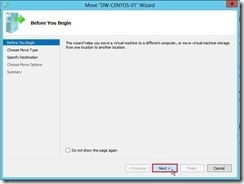 (3). On the Choose Move Type page, choose Move the virtual machine option next to click Next > button
(3). On the Choose Move Type page, choose Move the virtual machine option next to click Next > button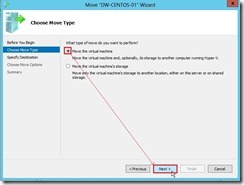 (4). On the Specify Destination Computer page, click Browse… button to search or enter a computer name
(4). On the Specify Destination Computer page, click Browse… button to search or enter a computer name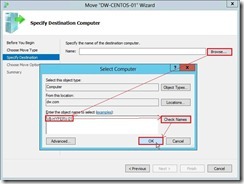 So does that the Destination Hyper-V Server as “VB-HYPERV-01” will be selected. Click Next > button to go ahead.
So does that the Destination Hyper-V Server as “VB-HYPERV-01” will be selected. Click Next > button to go ahead.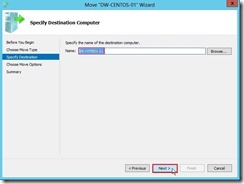 (5). On the Choose Move Options page, select Move the virtual machine’s data to single location option next to click Next > button.
(5). On the Choose Move Options page, select Move the virtual machine’s data to single location option next to click Next > button.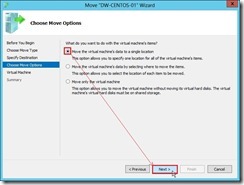 (6). On the Choose a new location for virtual machine page, click Browse… button to set Destination location folder next to click Next > button
(6). On the Choose a new location for virtual machine page, click Browse… button to set Destination location folder next to click Next > button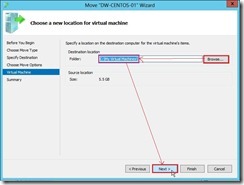 (7). Click Finish button to complete the Move Wizard.
(7). Click Finish button to complete the Move Wizard.
Reference:
(# 1) If we want to use remote management tool to manage Hyper-V in Windows 8, we can just install Hyper-V Manage Tools by Turn Windows feature on or off.

(# 2) What is firewall rule need to be created for live migration? How to do it by launching New Inbound Rule Wizard?
(1). In Rule Type page, select Custom option next to click Next > button
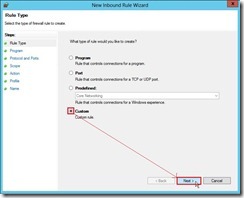 (2). In Program page, select This program path: option, write down %systemroot%\system32\vmms.exe next to click Customize… button
(2). In Program page, select This program path: option, write down %systemroot%\system32\vmms.exe next to click Customize… button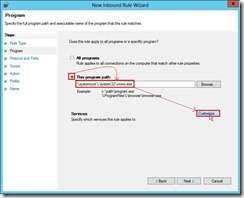 (3). In Customize Service Settings dialog box, select Apply to service with this service short name option, write down vmms word next to click OK button
(3). In Customize Service Settings dialog box, select Apply to service with this service short name option, write down vmms word next to click OK button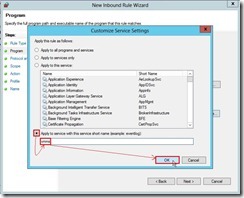 then click Next > button
then click Next > button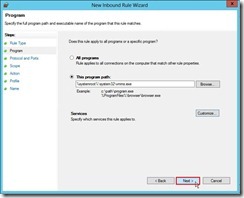 (4). In Protocol and Ports page, select TCP Protocol type and Specific Ports Local port with 6600 value next to click Next > button
(4). In Protocol and Ports page, select TCP Protocol type and Specific Ports Local port with 6600 value next to click Next > button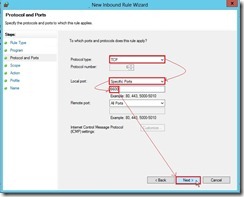 (5). In Scope page, click Next > button if want to keep the default setting.
(5). In Scope page, click Next > button if want to keep the default setting.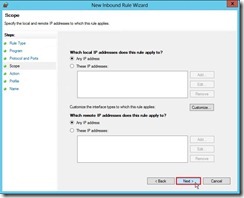 (6). In Action page, still click Next > button if no change anything
(6). In Action page, still click Next > button if no change anything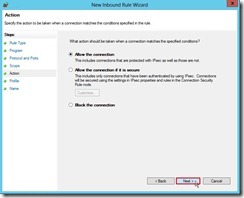 (7). In Profile page, select Domain, Private, Public check box for applying this rule next to click Next > button
(7). In Profile page, select Domain, Private, Public check box for applying this rule next to click Next > button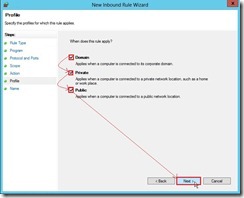 (8). Finally, assign a Name as “Hyper-V (MIG-TCP-In)” next to click Finish button to complete this wizard.
(8). Finally, assign a Name as “Hyper-V (MIG-TCP-In)” next to click Finish button to complete this wizard.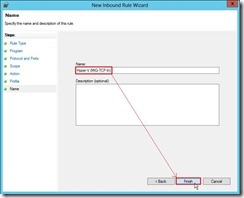 (9). Now the Inbound Rule for live migration has already been added.
(9). Now the Inbound Rule for live migration has already been added.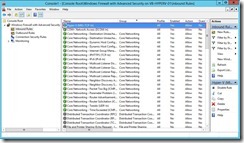
(# 3) If you cannot move a running VM, maybe we can try to power off VM next to move it again because the live migration also support offline status.
